本文中我们将开始介绍Native和JS之间的通信,我们会分别以以下的主线进行介绍:
1.初始化,启动过程
2.Native到JS的调用路径
3.JS到Native的调用路径
4.Native到JS的Callback回调路径
期间我们会看到各个部分的执行线程,存储的数据结构,Native的方法是如何映射到JS中的等信息…
我们先来看一下相关模块的初始化。在上一篇介绍ReactActivity的启动过程中,我们已经看到了Native和Js交互的入口在CatalysInstanceImpl的实现类中,我们分别看下CatalysInstanceImpl的构造过程和c++部分的启动入口OnLoad.cpp
private CatalystInstanceImpl {
...
mReactQueueConfiguration = ReactQueueConfigurationImpl.create(
reactQueueConfigurationSpec,
new NativeExceptionHandler());
initializeBridge(
new BridgeCallback(this),
jsExecutor,
mReactQueueConfiguration.getJSQueueThread(),
mNativeModulesQueueThread,
mNativeModuleRegistry.getJavaModules(this),
mNativeModuleRegistry.getCxxModules());
...
}
extern "C" JNIEXPORT jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* reserved) {
return initialize(vm, [] {
gloginit::initialize();
JSCJavaScriptExecutorHolder::registerNatives();
ProxyJavaScriptExecutorHolder::registerNatives();
CatalystInstanceImpl::registerNatives();
CxxModuleWrapperBase::registerNatives();
CxxModuleWrapper::registerNatives();
JCxxCallbackImpl::registerNatives();
NativeArray::registerNatives();
ReadableNativeArray::registerNatives();
WritableNativeArray::registerNatives();
NativeMap::registerNatives();
ReadableNativeMap::registerNatives();
WritableNativeMap::registerNatives();
ReadableNativeMapKeySetIterator::registerNatives();
#ifdef WITH_INSPECTOR
JInspector::registerNatives();
#endif
});
}
在c++部分的启动中,系统注册了一系列的jni方法提供和java层的基础交互。
在java层的初始化主要调用了initializeBridge 方法,initializeBridge又直接调用了jni的方法到c++部分,我们先来看下初始化的参数有哪些:
1.BridgeCallback 全局的回调函数,监听Bridge的一些行为
2.jsExecutor,实际上对应到c++中的JavaScriptHJSCJavaScriptExecutorHolder, 这个地方很难读,在java是一个JsExecutor实际上到了c++被映射成了JavaExecutorHolder,而JavaExecutorHolder用来生成一个JsExecutor的Factory,此处对应可以在OnLoad中发现蛛丝马迹 static constexpr auto kJavaDescriptor = “Lcom/facebook/react/bridge/JSCJavaScriptExecutor;”; 至于如何对应上的是facebook的Hybrid做的,没有深入研究。
3.mReactQueueConfiguration.getJSQueueThread(), 从名字上可以看到是JS的线程队列,我们先来看一下QueueThread的借口:
@DoNotStrip
public interface MessageQueueThread {
/**
* Runs the given Runnable on this Thread. It will be submitted to the end of the event queue even
* if it is being submitted from the same queue Thread.
*/
@DoNotStrip
void runOnQueue(Runnable runnable);
/**
* Runs the given Callable on this Thread. It will be submitted to the end of the event queue even
* if it is being submitted from the same queue Thread.
*/
@DoNotStrip
<T> Future<T> callOnQueue(final Callable<T> callable);
/**
* @return whether the current Thread is also the Thread associated with this MessageQueueThread.
*/
@DoNotStrip
boolean isOnThread();
/**
* Asserts {@link #isOnThread()}, throwing a {@link AssertionException} (NOT an
* {@link AssertionError}) if the assertion fails.
*/
@DoNotStrip
void assertIsOnThread();
/**
* Asserts {@link #isOnThread()}, throwing a {@link AssertionException} (NOT an
* {@link AssertionError}) if the assertion fails. The given message is appended to the error.
*/
@DoNotStrip
void assertIsOnThread(String message);
/**
* Quits this MessageQueueThread. If called from this MessageQueueThread, this will be the last
* thing the thread runs. If called from a separate thread, this will block until the thread can
* be quit and joined.
*/
@DoNotStrip
void quitSynchronous();
}
核心方法是runOnQueue和callOnQueue,分别传入Runnable 和 Callable,MessageQueueThread只有一个实现类,MessageQueueThreadImpl :
private final String mName;
private final Looper mLooper;
private final MessageQueueThreadHandler mHandler;
private final String mAssertionErrorMessage;
@DoNotStrip
@Override
public void runOnQueue(Runnable runnable) {
if (mIsFinished) {
FLog.w(
ReactConstants.TAG,
"Tried to enqueue runnable on already finished thread: '" + getName() +
"... dropping Runnable.");
}
mHandler.post(runnable);
}
可以看到内部是通过handler来实现线程队列的.
回过头来我们再来看JsQueueThread的初始化, JsQueueThread的初始化是在ReactQueueConfigurationImpl.create方法中创建的:
public static MessageQueueThreadImpl create(
MessageQueueThreadSpec spec,
QueueThreadExceptionHandler exceptionHandler) {
switch (spec.getThreadType()) {
case MAIN_UI:
return createForMainThread(spec.getName(), exceptionHandler);
case NEW_BACKGROUND:
return startNewBackgroundThread(spec.getName(), spec.getStackSize(), exceptionHandler);
default:
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown thread type: " + spec.getThreadType());
}
}
根据传入的spec来决定创建在UI线程还是新的线程中,spec的设置可以在ReactInstanceManager的createReactContext中找到,调用的是ReactQueueConfigurationSpec.createDefault()方法,createDefault中默认的是使用BackThreadSpeck, 即启动后台线程。
4.nMativeModulesQueueThread NativeModules的执行线程 初始化过程同jsQueueThread也是默认启动的后台线程
5.mNativeModuleRegistry.getJavaModules Native注册的所有的JavaModules,构建过程可以在createReactContet中的processPackages中找到,我们就不具体分析了,感兴趣可以自行查阅。
6.mNativeModuleRegistry.getCxxModules() 同上。
下面我们进入c++的部分,查看下c++部分的具体实现,我们先来看react/jni/CatalystInstanceImpl.cpp中的initializeBridge方法:
void CatalystInstanceImpl::initializeBridge(
jni::alias_ref<ReactCallback::javaobject> callback,
// This executor is actually a factory holder.
JavaScriptExecutorHolder* jseh,
jni::alias_ref<JavaMessageQueueThread::javaobject> jsQueue,
jni::alias_ref<JavaMessageQueueThread::javaobject> nativeModulesQueue,
jni::alias_ref<jni::JCollection<JavaModuleWrapper::javaobject>::javaobject> javaModules,
jni::alias_ref<jni::JCollection<ModuleHolder::javaobject>::javaobject> cxxModules) {
// TODO mhorowitz: how to assert here?
// Assertions.assertCondition(mBridge == null, "initializeBridge should be called once");
moduleMessageQueue_ = std::make_shared<JMessageQueueThread>(nativeModulesQueue);
// This used to be:
//
// Java CatalystInstanceImpl -> C++ CatalystInstanceImpl -> Bridge -> Bridge::Callback
// --weak--> ReactCallback -> Java CatalystInstanceImpl
//
// Now the weak ref is a global ref. So breaking the loop depends on
// CatalystInstanceImpl#destroy() calling mHybridData.resetNative(), which
// should cause all the C++ pointers to be cleaned up (except C++
// CatalystInstanceImpl might be kept alive for a short time by running
// callbacks). This also means that all native calls need to be pre-checked
// to avoid NPE.
// See the comment in callJSFunction. Once js calls switch to strings, we
// don't need jsModuleDescriptions any more, all the way up and down the
// stack.
moduleRegistry_ = std::make_shared<ModuleRegistry>(
buildNativeModuleList(
std::weak_ptr<Instance>(instance_),
javaModules,
cxxModules,
moduleMessageQueue_));
instance_->initializeBridge(
folly::make_unique<JInstanceCallback>(
callback,
moduleMessageQueue_),
jseh->getExecutorFactory(),
folly::make_unique<JMessageQueueThread>(jsQueue),
moduleRegistry_);
}
其中2个重要部分是 用传入的Modules创建了一个ModuleRegistry对象,调用了ReactCommon/cxxreact/Instance的initializeBridge方法
我们先来看ModuleRegistry对象,顾名思义可以理解这里是Module的仓库,存放了所有java层传入的Module,在ModuleRegistry的构造函数什么也没有做只是记录下了modules,其中提供了一个updateModuleNamesFromIndex, 会生成一个modulesByName_[]的数据结构用来根据名称去除index,即Module的Id。其中还提供了registerModules方法,可以支持在构造外的注入Module,具体的使用我们就不做分析了。
我们再来看Instance重的initializeBridge方法
void Instance::initializeBridge(
std::unique_ptr<InstanceCallback> callback,
std::shared_ptr<JSExecutorFactory> jsef,
std::shared_ptr<MessageQueueThread> jsQueue,
std::shared_ptr<ModuleRegistry> moduleRegistry) {
callback_ = std::move(callback);
moduleRegistry_ = std::move(moduleRegistry);
jsQueue->runOnQueueSync([this, &jsef, jsQueue]() mutable {
nativeToJsBridge_ = folly::make_unique<NativeToJsBridge>(
jsef.get(), moduleRegistry_, jsQueue, callback_);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m_syncMutex);
m_syncReady = true;
m_syncCV.notify_all();
});
CHECK(nativeToJsBridge_);
}
在方法中,系统调用jsQueue(之间在java层传入的JsQueuThread),的run方法,在js线程中继续之后的行为,在线程中系统创建了NativeToJsBridge对象(和js交互的Bridge)
NativeToJsBridge::NativeToJsBridge(
JSExecutorFactory* jsExecutorFactory,
std::shared_ptr<ModuleRegistry> registry,
std::shared_ptr<MessageQueueThread> jsQueue,
std::shared_ptr<InstanceCallback> callback)
: m_destroyed(std::make_shared<bool>(false))
, m_delegate(std::make_shared<JsToNativeBridge>(registry, callback))
, m_executor(jsExecutorFactory->createJSExecutor(m_delegate, jsQueue))
, m_executorMessageQueueThread(std::move(jsQueue)) {}
在NativeToJsBridge的构造函数中,主要调用了jsExecutorFactory创建了一个JSExecutor, jsExecutorFactory就是java层传入的JsExecutor(所以说这里很坑,明明是JsExecutor对引导c++部分就变成了JsExecutorFactory),在查看OnLoad.cpp中的可以看到实际调用的是AndroidJSCFactory的makeAndroidJSCExecutorFactory, 是一个JSCExecutorFacory对象,JSCExecutorFacotry的实现在JSCExecutor.cpp文件中,实际上创建了一个JSCExecutor我们来看一下JSCExecutor的构造:
JSCExecutor::JSCExecutor(std::shared_ptr<ExecutorDelegate> delegate,
std::shared_ptr<MessageQueueThread> messageQueueThread,
const folly::dynamic& jscConfig) throw(JSException) :
m_delegate(delegate),
m_messageQueueThread(messageQueueThread),
m_nativeModules(delegate ? delegate->getModuleRegistry() : nullptr),
m_jscConfig(jscConfig) {
initOnJSVMThread();
{
SystraceSection s("nativeModuleProxy object");
installGlobalProxy(m_context, "nativeModuleProxy",
exceptionWrapMethod<&JSCExecutor::getNativeModule>());
}
}
可以看到这里有一个delegate delegate可以在NativeToJsBridge的构造函数中看到,是一个JsToNativeBridge对象。里面记录了一个ModuleRegistry。
我们总结一些初始化的工作:
1.创建了一个NativeToJsBridge对象
2.创建了一个JSCExecutor用来和JS交互
3.将本地的Module记录到ModuleRegistry中,已数组的index作为module的ID
初始化完了我们来看一下从JAVA获取JavaScriptModule开始到执行JS方法的过程,我们从ReactContext的getJSModule开始看起,它调用了CatalysInstanceImpl的getJSModule方法,在CatalysInstanceImpl中又调用到了JavaScriptModuleRegistry的getJavaScriptModule方法:
public synchronized <T extends JavaScriptModule> T getJavaScriptModule(
CatalystInstance instance,
Class<T> moduleInterface) {
JavaScriptModule module = mModuleInstances.get(moduleInterface);
if (module != null) {
return (T) module;
}
JavaScriptModule interfaceProxy = (JavaScriptModule) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
moduleInterface.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{moduleInterface},
new JavaScriptModuleInvocationHandler(instance, moduleInterface));
mModuleInstances.put(moduleInterface, interfaceProxy);
return (T) interfaceProxy;
}
内部实现使用了动态代理最终在调用方法时候走入到了JavaScriptModuleInvocationHandler中, 然后又触发到了CatalystInstanceImpl中的callFunction方法,然后进入了c++部分,调用Instance的callFunction方法,调用NativeToJsBridge的callFunction方法 :
void NativeToJsBridge::callFunction(
std::string&& module,
std::string&& method,
folly::dynamic&& arguments) {
int systraceCookie = -1;
#ifdef WITH_FBSYSTRACE
systraceCookie = m_systraceCookie++;
FbSystraceAsyncFlow::begin(
TRACE_TAG_REACT_CXX_BRIDGE,
"JSCall",
systraceCookie);
#endif
runOnExecutorQueue([module = std::move(module), method = std::move(method), arguments = std::move(arguments), systraceCookie]
(JSExecutor* executor) {
#ifdef WITH_FBSYSTRACE
FbSystraceAsyncFlow::end(
TRACE_TAG_REACT_CXX_BRIDGE,
"JSCall",
systraceCookie);
SystraceSection s("NativeToJsBridge::callFunction", "module", module, "method", method);
#endif
// This is safe because we are running on the executor's thread: it won't
// destruct until after it's been unregistered (which we check above) and
// that will happen on this thread
executor->callFunction(module, method, arguments);
});
}
然后调用了runOnExecutorQueue(实际上是Java层创建的MessageQueueThread , 即js线程),将具体的执行放入js线程队列,在线程中调用JSCExecutor的callFunction方法执行具体的方法,在JSExecutor中,JSExecutor通过global设置的属性来获取js中的方法以实现和js的交互,JSExecutor的callFunction如下:
void JSCExecutor::callFunction(const std::string& moduleId, const std::string& methodId, const folly::dynamic& arguments) {
SystraceSection s("JSCExecutor::callFunction");
// This weird pattern is because Value is not default constructible.
// The lambda is inlined, so there's no overhead.
auto result = [&] {
JSContextLock lock(m_context);
try {
if (!m_callFunctionReturnResultAndFlushedQueueJS) {
bindBridge();
}
return m_callFunctionReturnFlushedQueueJS->callAsFunction({
Value(m_context, String::createExpectingAscii(m_context, moduleId)),
Value(m_context, String::createExpectingAscii(m_context, methodId)),
Value::fromDynamic(m_context, std::move(arguments))
});
} catch (...) {
std::throw_with_nested(
std::runtime_error("Error calling " + moduleId + "." + methodId));
}
}();
callNativeModules(std::move(result));
}
先判断js中的方法是否获取到,没有的话就调用bindBridge方法,bindBridge中从global中获取js的方法。 bind结束后调用了m_callFunctionReturnFlushedQueueJs方法,即JS中的callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue方法, js中的对应方法主要调用了2个方callFuncion和flushedQueue,我们先来看一下callFunction方法,对应的方法存在于BatchedBridge下的MessageQueue.js文件中:
__callFunction(module: string, method: string, args: any[]): any {
this._lastFlush = new Date().getTime();
this._eventLoopStartTime = this._lastFlush;
Systrace.beginEvent(`${module}.${method}()`);
if (this.__spy) {
this.__spy({type: TO_JS, module, method, args});
}
const moduleMethods = this.getCallableModule(module);
invariant(
!!moduleMethods,
'Module %s is not a registered callable module (calling %s)',
module,
method,
);
invariant(
!!moduleMethods[method],
'Method %s does not exist on module %s',
method,
module,
);
const result = moduleMethods[method].apply(moduleMethods, args);
Systrace.endEvent();
return result;
}
getCallableModule方法直接从_lazyCallableModules中取出对应的Module,而在registerCallableModule的时候会将module记录在_lazyCallableModules中,它记录了所有的jsModule。获取到Module中的所有方法后通过方法名获取到具体的方法然后调用apply开始执行方法。
我们可以用一张序列图来表示执行的过程:
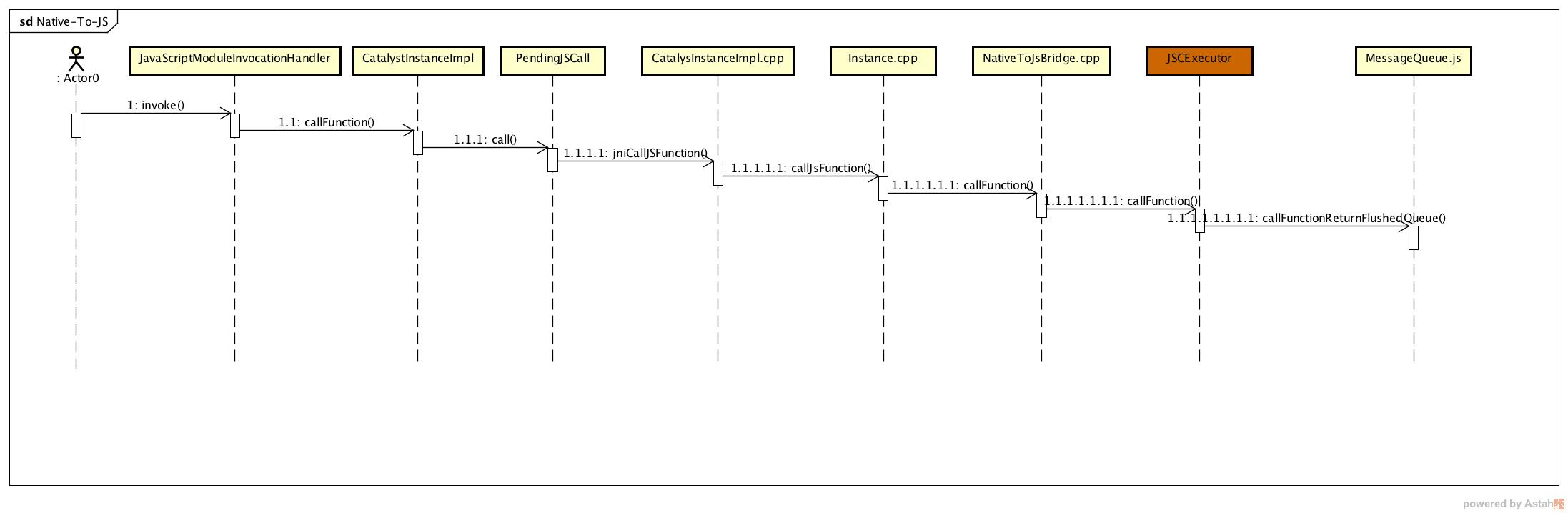
我们再来看一下从jS到Native层的调用,我们从NativeModules.js看起
let NativeModules : {[moduleName: string]: Object} = {};
if (global.nativeModuleProxy) {
NativeModules = global.nativeModuleProxy;
} else {
const bridgeConfig = global.__fbBatchedBridgeConfig;
invariant(bridgeConfig, '__fbBatchedBridgeConfig is not set, cannot invoke native modules');
const defineLazyObjectProperty = require('defineLazyObjectProperty');
(bridgeConfig.remoteModuleConfig || []).forEach((config: ModuleConfig, moduleID: number) => {
// Initially this config will only contain the module name when running in JSC. The actual
// configuration of the module will be lazily loaded.
const info = genModule(config, moduleID);
if (!info) {
return;
}
if (info.module) {
NativeModules[info.name] = info.module;
}
// If there's no module config, define a lazy getter
else {
defineLazyObjectProperty(NativeModules, info.name, {
get: () => loadModule(info.name, moduleID)
});
}
});
}
可以看到js中对所有的nativeModule都调用了genModule方法生成Module对象,然后通过genMethod生成方法,当方法调用时 实际上调用了BatchedBridge.enqueueNativeCall方法:
const BatchedBridge = new MessageQueue(
// $FlowFixMe
typeof __fbUninstallRNGlobalErrorHandler !== 'undefined' &&
__fbUninstallRNGlobalErrorHandler === true, // eslint-disable-line no-undef
);
BatchedBridge实际上是MessageQueue对象,在MessageQueue中有几个重要的数据结构:
_queue: [number[], number[], any[], number];
_successCallbacks: (?Function)[];
_failureCallbacks: (?Function)[];
_callID: number;
其中queue记录了所有还没有被执行的方法,4个参数分别表示 moduleId, methodId, callId, 其中mouduleId 和 methodid实际上都是c++中存储的Module的下标。我们接着看enqueueNativeCall方法:
this._callId++;
if (onFail || onSucc) {
onFail && params.push(this._callID << 1);
onSucc && params.push((this._callID << 1) | 1);
this._successCallbacks[this._callID] = onSucc;
this._failureCallbacks[this._callID] = onFail;
}
global.nativeFlushQueueImmediate(queue);
核心代码入上图所示,如果从在回调的onFail和onSucc方法则分别加入到successCallbacks和failureCallbacks中,index为callId, callId是一个自增的计数器,然后如果是onFail方法则在params中加入_callId左移一位,onSucc则左移一位末尾补1,即使用_callId的最后一位用来标识是否存在回调方法。
gloal.nativeFlushQueueImmediate方法实际绑定JSCExecutor中的对应方法:
void JSCExecutor::flushQueueImmediate(Value&& queue) {
auto queueStr = queue.toJSONString();
m_delegate->callNativeModules(*this, folly::parseJson(queueStr), false);
}
然后调用m_delegate的callNativeModules方法,之前我们分析过这里的m_delegate实际上是JSToNativeBridge对象,我们来看其中的方法:
void callNativeModules(
JSExecutor& executor, folly::dynamic&& calls, bool isEndOfBatch) override {
CHECK(m_registry || calls.empty()) <<
"native module calls cannot be completed with no native modules";
m_batchHadNativeModuleCalls = m_batchHadNativeModuleCalls || !calls.empty();
// An exception anywhere in here stops processing of the batch. This
// was the behavior of the Android bridge, and since exception handling
// terminates the whole bridge, there's not much point in continuing.
for (auto& call : parseMethodCalls(std::move(calls))) {
m_registry->callNativeMethod(call.moduleId, call.methodId, std::move(call.arguments), call.callId);
}
if (isEndOfBatch) {
// onBatchComplete will be called on the native (module) queue, but
// decrementPendingJSCalls will be called sync. Be aware that the bridge may still
// be processing native calls when the birdge idle signaler fires.
if (m_batchHadNativeModuleCalls) {
m_callback->onBatchComplete();
m_batchHadNativeModuleCalls = false;
}
m_callback->decrementPendingJSCalls();
}
}
这里将js传入的queue中的数据全部取出来然后依次调用registry的callNativeMethod方法,registry中又根据moduleID去除具体的module然后调用invoke方法,可以看NativeModule方法中的invoke方法,NativeModule的实现类是JavaModuleWrapper,我们来看具体的方法实现
void JavaNativeModule::invoke(unsigned int reactMethodId, folly::dynamic&& params, int callId) {
messageQueueThread_->runOnQueue([this, reactMethodId, params=std::move(params), callId] {
static auto invokeMethod = wrapper_->getClass()->getMethod<void(jint, ReadableNativeArray::javaobject)>("invoke");
#ifdef WITH_FBSYSTRACE
if (callId != -1) {
fbsystrace_end_async_flow(TRACE_TAG_REACT_APPS, "native", callId);
}
#endif
invokeMethod(
wrapper_,
static_cast<jint>(reactMethodId),
ReadableNativeArray::newObjectCxxArgs(std::move(params)).get());
});
}
使用了messageQueueThread(实际上是java传入的NativeModule的执行线程队列控制),然后走到了java中对应的JavaMethodWrapper中,在其将数据进行转换并使用反射调用了具体的方法。
如果带有callId的参数将被转换成Callback对象,当调用Callback对象的invoke方法时会走到CatalystyInstanceImpl中的invokeJsCallback方法最终通过一系列调用(同callFunction)最终走到js线程中,并执行JSCExecutor的InvockCallback方法,实际上又走入了JS的invokeCallbackAndReturnFlushQueue方法中,我们直接来看hs中的方法,js中又走了2步invokeCallback和flushQueue ,flushQueue我们就不在讲述,直接来看invokeCallback
__invokeCallback(cbID: number, args: any[]) {
this._lastFlush = new Date().getTime();
this._eventLoopStartTime = this._lastFlush;
// The rightmost bit of cbID indicates fail (0) or success (1), the other bits are the callID shifted left.
// eslint-disable-next-line no-bitwise
const callID = cbID >>> 1;
// eslint-disable-next-line no-bitwise
const isSuccess = cbID & 1;
const callback = isSuccess
? this._successCallbacks[callID]
: this._failureCallbacks[callID];
if (__DEV__) {
const debug = this._debugInfo[callID];
const module = debug && this._remoteModuleTable[debug[0]];
const method = debug && this._remoteMethodTable[debug[0]][debug[1]];
if (!callback) {
let errorMessage = `Callback with id ${cbID}: ${module}.${method}() not found`;
if (method) {
errorMessage =
`The callback ${method}() exists in module ${module}, ` +
'but only one callback may be registered to a function in a native module.';
}
invariant(callback, errorMessage);
}
const profileName = debug
? '<callback for ' + module + '.' + method + '>'
: cbID;
if (callback && this.__spy) {
this.__spy({type: TO_JS, module: null, method: profileName, args});
}
Systrace.beginEvent(
`MessageQueue.invokeCallback(${profileName}, ${stringifySafe(args)})`,
);
}
if (!callback) {
return;
}
this._successCallbacks[callID] = this._failureCallbacks[callID] = null;
callback(...args);
if (__DEV__) {
Systrace.endEvent();
}
}
可以看到其中根据callId的最后一位确定调用的是onFail还是onSucc然后从对应的队列中执行找到对应的js方法然后执行。
JsToNative的调用过程如下图:
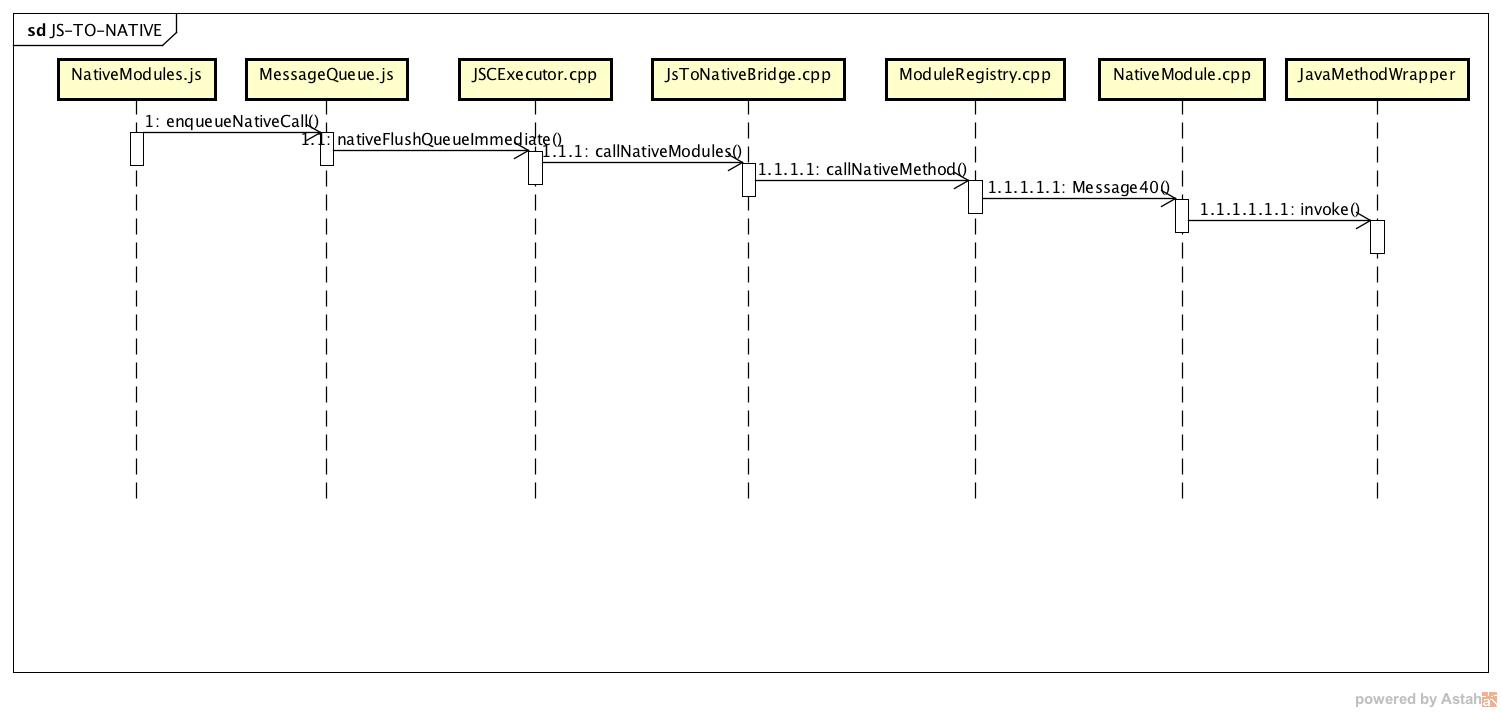
我对本文中涉及到的类画了一个简单的类图可以作为参照:
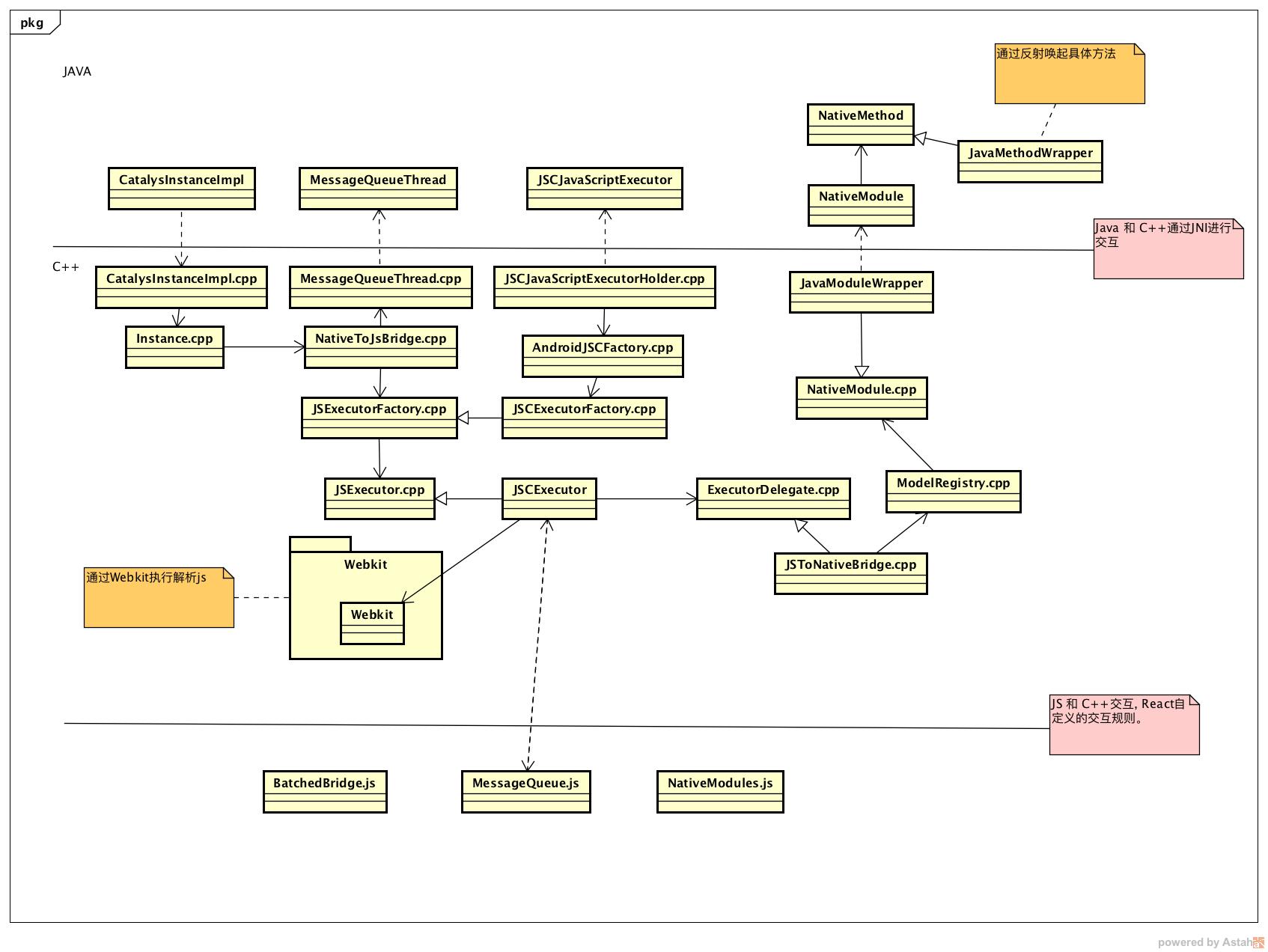
欢迎关注我的微信公众号
璐豪笔记
